WHAT ARE INTERNET AND INTRANET AND EXTRANET
Internet, intranet, and extranet are three terms that describe “Internet-type” applications that are used by an organization.
INTERNET:
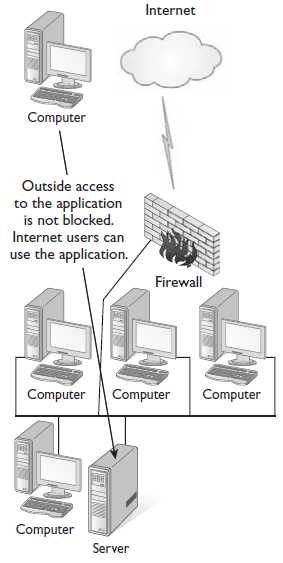
If you wish to expose information to everyone in the world, then you would build an Internet-type application. An Internet-type application uses Internet protocols such as HTTP, FTP, or SMTP and is available to persons anywhere on the Internet. We use the Internet and web applications as ways to extend who the application can reach. For example, I no longer need to go to the bank to transfer funds. Because the bank has built a website on the Internet, I can do that from the comfort of my own home.
INTRANET:
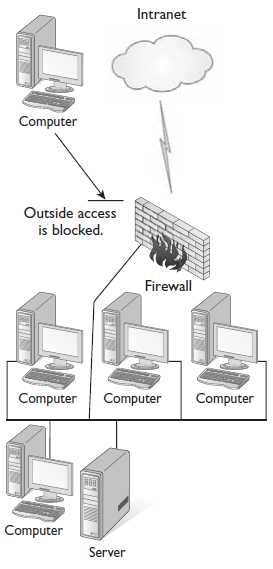
An application is considered to be on the company’s intranet if it is using Internet-type protocols such as HTTP or FTP but the application is available only within the company. The information on a company’s intranet would not be accessible to persons on the Internet because it is not for public use. For example, a few years ago I was sitting with my banking officer going over my account and noticed that the bank had moved all of its customer account information to a website and that the banking officer was using a web browser to retrieve my account details. Although the application was being used by a web browser, it was still an “internal” application meant only for banking officers.
EXTRANET:
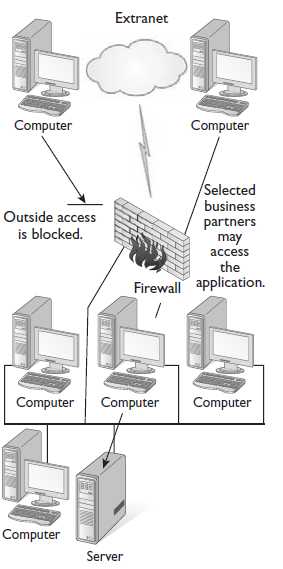
From time to time, an application that has been built for the company’s intranet and used by internal employees will need to be extended to select business partners or customers. If you extend your intranet out to select business partners or customers, you have created an extranet. An extranet cannot be used by anyone else external to the company except for those selected individuals. The figure displays the basic configurations of the Internet, intranet, and extranet.
 |
Difference Between the Internet and Intranet
| Internet | Intranet |
| The Internet is a huge network that connects computer networks across the world. It uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP). | An intranet is a network connection similar to the internet but it is limited by the users within an organization. It can include several LANs or leased lines in the wide-area network. |
| The internet enables the exchange of a huge amount of (unlimited) information between connected users. | It enables the exchange of limited information between limited and authorized people of a particular firm. |
| It provides access to all types of information. | The intranet has all the information, resources, programs, events, and more related to a company. |
| It is a public network. | It is a private network. |
| The internet has multiple users. Anyone can access it. | Intranet has are limited users. Only certain people with login credentials are authorized to use Intranet. |
| The Internet consists of several intranets. | It is like a part of the Internet. |
| It is a wide and insecure network. The Internet is a global network with low privacy. There is the possibility of leaks of data and information | An intranet is a limited and secure network. It has a pre-installed firewall that protects the privacy of the firm against unauthorized access or hackers. |
Also read,