Soap Manufacturing Process
Soaps are from the class of surface-active agents or surfactants. Where the surface properties play the role of water-like and dislike ability of the compound. A compound that shows attractiveness towards the water and dissolves in it is called a hydrophilic compound and the opposite action of which the compound repels water and does not dissolve but stays separately forming another layer and may dissolve organic compounds is called hydrophobic. By using this mechanism a surfactant is a molecule that has these two compounds as head and tail and acts like a link binder between the water and dirt or oil.
Soaps are chemical compounds of the type R.COO.M where the part “R.COO” is fatty acid radical representing oleic, stearic, palmitic, lauric, and myristic. These are usually present in soaps as a mixture based on glyceride raw materials. ‘M’ is an alkali element such as Na or K.
Types of the soap manufacturing process:
1. Batch saponification process:
The most famous Twirchell process is where acid hydrolysis of glycerides is done along with alkali addition, or even by direct saponification using concentrated caustic. This process is used for small-scale and domestic-level production
2. Continuous Hydrolysis and Saponification Process: This is followed for industrial large-scale production.
Chemical Reactions:
Fat splitting:
(R.COO)3.C3H5 + 3H2O à 3R.COO.H + C3H5(OH)3
Saponification:
R.COO.H + M.OH à R.COO.M + H2O
Where M is mostly alkali earth metal Na and K
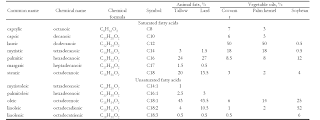
Raw materials: Soaps are derived from triglycerides, a compound having three ester-linked fatty oils and alkali earth metal hydroxides like caustic soda or potassium hydroxide. The fatty acid molecule present in the oil is the main part of starting material.
Process flow sheet:
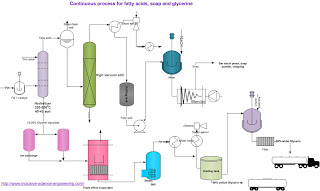
General Consideration of Raw Materials in Soap Making Process
Soaps are manufactured from fatty acids and oil for a variety of soap products


